|

THE CONSTITUTION
OF THE
DEMOCRATIC SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF SRI LANKA
(As amended up to
29th October 2020)
Revised Edition – 2021
Published by the Parliament Secretariat
This unofficial edition edited by the Bills Office of the
Legislative Services Department of Parliament of Sri Lanka
reproduces the text of the Constitution of the Democratic Socialist
Republic of Sri Lanka as amended by Parliament from time to time up
to the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution. The footnotes below
the text indicate the particular Amendments to the Constitution by
which such Amendments have been made
SVASTIThe PEOPLE OF SRI LANKA having, by
their Mandate freely expressed and granted on the sixth day of the
waxing moon in the month of Adhi Nikini in the year two thousand
five hundred and twenty one of the Buddhist Era (being Thursday the
twenty-first day of the month of July in the year one thousand nine
hundred and seventy seven), entrusted to and empowered their
Representatives elected on that day to draft, adopt and operate a
new Republican Constitution in order to achieve the goals of a
DEMOCRATIC SOCIALIST REPUBLIC, and having solemnly resolved by the
grant of such Mandate and the confidence reposed in their said
Representatives who were elected by an overwhelming majority, to
constitute SRI LANKA into a DEMOCRATIC SOCIALIST REPUBLIC whilst
ratifying the immutable republican principles of REPRESENTATIVE
DEMOCRACY and assuring to all Peoples FREEDOM, EQUALITY, JUSTICE,
FUNDAMENTAL HUMAN RIGHTS and the INDEPENDENCE OF THE JUDICIARY as
the intangible heritage that guarantees the dignity and well-being
of succeeding generations of the People of SRI LANKA and of all the
People of the World, who come to share with those generations the
effort of working for the creation and preservation of a JUST AND
FREE SOCIETY:
WE, THE FREELY ELECTED REPRESENTATIVES OF THE
PEOPLE OF SRI LANKA, in pursuance of such Mandate, humbly
acknowledging our obligations to our People and gratefully
remembering their heroic and unremitting struggle to regain and
preserve their rights and privileges so that the Dignity and Freedom
of the Individual may be assured, Just, Social, Economic and
Cultural Order attained, the Unity of the Country restored, and
Concord established with other Nations,
do hereby adopt and enact
this
CONSTITUTION
as the
SUPREME LAW
of the
DEMOCRATIC SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF SRI LANKA
|
|
|
|
CHAPTER XXI
TRANSITIONAL PROVISIONS |
First Presiden
[4, 3 of 1982]
|
|
160. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in any
other provision of the Constitution, the person holding the
office of President immediately before the commencement of
the Constitution shall be the first President under the
Constitution and shall be deemed for all purposes to have
been elected as the President of the Republic, and 145[shall,
subject to the provisions of Article 31, hold office] for a period
of six years from February 4, 1978.
The President shall, notwithstanding the provisions of
Article 32, be deemed to have assumed office immediately upon
the commencement of the Constitution and shall be entitled
thereupon to exercise, perform and discharge all the powers,
duties and functions conferred or imposed on, or assigned to, the
President by the Constitution or otherwise. The President shall,
as soon as possible thereafter at a sitting of Parliament, take and
subscribe the oath or make and subscribe the affirmation set out
in the Fourth Schedule
|
First Parliament
[2, 2 of 1979]
[4, 6 of 1983]
[2, 5 of 1983]
[2, 4 of 1982]
|
|
161. Notwithstanding anything to the contray in any other provision of the Constitution -
(a) the first Parliament shall consist, of one
hundred and sixty-eight members and subject to the succeeding provisions of this Article, all
persons who immediately before the commencement of the Constitution were members of the National State Assembly shall
be deemed to have been elected as Members of Parliament;
(b)
(i) if the election, as a Member of the
National State Assembly, of a person
deemed to have been elected to the first
Parliament is declared void under the
law for the time being in force and no
other person is determined to have
been duly returned or elected, the seat of
such Member shall be vacant, and an
election to the electoral district as
existing immediately prior to the
commencement of the Constitution, shall
be held in accordance with the law
relating to elections to the National State
Assembly in force immediately before the Commencement of the Constitution and
on the basis of the register of electors
applicable to such electoral district which was
operative on the day immediately preceding
the commencement of the Constitution;
(ii) the law applicable to election petitions
in relation to an election held as provided in
sub- paragraph (i) shall be the law in force
upon the commencement of the Constitution
and in the event of such an election being
declared void the provisions of sub-paragraph
(i) shall, mutatis mutandis, apply;
(c) if the election as a Member of the National
State Assembly of a person who is deemed to have been elected to the first Parliament is
declared void or undue and any other person is determined to have been duly returned or elected
such other person shall be deemed to have been duly elected as a Member of the first Parliament;
(d)
(i) where immediately before the commencement
of Constitution there was a vacancy in the
membership of the National State Assembly
or where a vacancy in the membership of
the first Parliament occurs otherwise than
under the provisions of paragraph (b) of this
Article, such vacancy shall be filled in the
manner provided in sub-paragraph (iii) hereof;
146[(ii) where during the duration of the First
Parliament, a Member ceases, by
resignation, expulsion or otherwise, to be a
member of the recognized political party to
which he belonged upon or after the
commencement of the Constitution, the
Secretary of such party shall, within two
weeks of the date on which such Member so
ceased to be a member of such party,
communicate, in writing to the SecretaryGeneral of Parliament, the fact and date thereof.
The Secretary-General shall, upon receipt
of such communication, submit it to the
Speaker.
Where a Member ceases to be a member of the
recognized political party to which he belonged
by reason of being expelled from such party, he
shall be entitled to apply, within one month of
the date of such expulsion by petition in writing,
to the Supreme Court for a determination that
such expulsion was invalid. In the event of any
such application being made, the Registrar of
the Supreme Court shall forthwith inform the
Secretary-General of Parliament in writing, of
such application, every such application shall
be heard and determined by not less than three
Judges of the Supreme Court who shall, within
two months of the making of such application,
determine whether such expulsion was valid or
not.
The Speaker shall, on receiving in the
aforesaid manner, a communication alleging
that a Member has ceased to be a member of
the recognized political party to which such
Member belonged, appoint a Select Committee
consisting of not less than five Members of
Parliament (one of whom shall be nominated as
Chairman thereof) to inquire into, and report to
Parliament on, the circumstances in which such
Member is alleged to have resigned from, or to
have been expelled from, or to have otherwise
ceased to be a member of, such party, and the
reasons therefor:
Provided, however, that where such
communication alleges that a Member has ceased
to be a member of the recognized political party
to which he belonged by reason of his being
expelled therefrom, no Select Committee shall be
appointed as aforesaid until after the expiration
of a period of one month from the date of such
alleged expulsion, and in any case where such
Member has applied to the Supreme Court for a
determination that such expulsion was invalid,
unless and until the Supreme Court has
determined that such expulsion was valid.
The provisions of the Parliament (Powers and
Privileges) Act shall, mutatis mutandis, apply
in relation to proceedings before, and to the
privileges, immunities and powers of, a Select
Committee appointed as aforesaid and every
such Select Committee shall be deemed, for
the purposes of that Act, to be duly authorized
by an order of Parliament to send for persons,
papers and records.
After consideration of the report made by
a Select Committee appointed as aforesaid,
Parliament may, by resolution passed by not
less than eighty-five Members voting in its
favour, resolve that the Member to whom such
report relates, shall cease to be a Member of
Parliament. The Speaker shall endorse on
every resolution so passed, a certificate in
the following form:–
“This resolution has been passed by the
majority required by Article 161(d) (ii) of the
Constitution”.
The seat of such Member shall, with effect from
the date of such certificate, become vacant.
Every such certificate shall be conclusive
for all purposes and shall not be questioned in
any court, and no court or tribunal shall
inquire into, pronounce upon or in any manner
call in question, the validity of the resolution on
which such certificate is endorsed on any
ground whatsoever.]
(iii) Where a vacancy as is referred to in subparagraph (i) or
(ii) has occurred, the SecretaryGeneral of Parliament shall forthwith inform
the Commissioner of Elections of such vacancy.
The Commissioner of Elections shall thereupon
require the Secretary of the political party to
which such Member belonged to nominate a
member of such party 147[to fill such vacancy.
A nomination made by the Secretary of such
political party under this sub-paragraph shall
be accompanied by an oath or affirmation, as
the case may be, in the form set out in the
Seventh Schedule, taken and subscribed or
made and subscribed, as the case may be, by
the person nominated to fill such vacancy. Upon
the receipt of such nomination, accompanied by
such oath or affirmation the Commissioner]
shall declare such person to be the Member for
the electoral district in respect of which the
vacancy occurred:
148[Provided that where the Secretary of
such political party fails to nominate a
member of such political party to fill such
vacancy under the preceding provisions of this
sub-paragraph 149[within thirty days of his
being required to do so and in the aforesaid
manner] or where the Secretary of a political
party had been required, before the coming
into force of this proviso, to nominate a
member of such political party to fill any such
vacancy under such provisions and such
Secretary fails, within thirty days of the
coming into force of this proviso, to nominate a
member of such political party to fill such
150[vacancy, or where such political party is
deemed to be prescribed under Article 157(a),
then, the Commissioner of Elections] shall
forthwith so inform the President, who shall,
within thirty days of the receipt by him of
such information, by Notice published in the
Gazette order the Commissioner of Elections
to hold an election for the electoral district
in respect of which such vacancy has occurred.
The Commissioner of Elections shall thereupon
hold an election, in accordance with Part I and
Parts IV to VI (both inclusive) of the Ceylon
(Parliamentary Elections) Order in Council,
1946, for such electoral district as existed immediately preceding the Constitution and on
the basis of such part of the register, prepared
under the Registration of Electors Act, No. 44 of
1980, and in operation, as corresponds to such
electoral district. The aforesaid parts of the
Ceylon (Parliamentary Elections) Order in
Council, 1946, shall, for the purposes of such
election and notwithstanding the repeal of such
Order in Council, be deemed to be in force and
shall, mutatis mutandis and except as otherwise
expressly provided in the Constitution, apply to
such election.
The law applicable to election petitions in relation
to such electoral district shall be the aforesaid
parts of such Order in Council as applied
aforesaid and in the event of such election being
declared void and no other person is determined to
have been duly returned or elected, the election to
fill such vacancy shall be held in accordance
with the provisions of this proviso.]
151[(iv) Where a Member nominated or elected
to fill any such vacancy as is referred to in
sub-paragraph (i) or sub-paragraph (ii), being a
Member who has taken and subscribed or made
and subscribed an oath or affirmation in the
form set out in the Seventh Schedule, directly or
indirectly, in or outside Sri Lanka, supports,
espouses, promotes, finances, encourages or
advocates the establishment of a separate State
within the territory of Sri Lanka, any person may
make an application to the Court of Appeal for a
declaration that such member has directly or
indirectly, in or outside Sri Lanka, supported,
espoused, promoted, financed, encouraged or
advocated the establishment of a separate State
within the territory of Sri Lanka.
If the Court of Appeal makes, on such application,
a declaration that such Member has directly or
indirectly, in or outside Sri Lanka, supported,
espoused, promoted, financed, encouraged or
advocated the establishment of a separate State
within the territory of Sri Lanka, the seat of such
Member shall be deemed to be vacant with effect
from the date of such declaration and such
Member shall be disqualified from sitting and
voting in Parliament and from being elected or
nominated to Parliament for a period of seven
years from the date of such declaration. The
vacancy occurring in the membership of
Parliament by reason of such declaration shall be
filled in the manner provided in paragraph (iii).
The jurisdiction of the Court of Appeal in respect
of its powers under this sub-paragraph shall be
exercised in the manner provided in subparagraph (iv) of the proviso to paragraph (2) of
Article 146.]
152(e) [Unless sooner dissolved, the First Parliament
shall continue until August 4, 1989 and no longer and shall thereupon stand dissolved, and the provisions of Article 70(5)(b) shall, mutatis
mutandis, apply.]
|
|
Application of
certain
provisions |
|
162.
(1) The provisions of Article 98, other than
paragraphs (8) and (9) thereof, and Article 99 shall not come
into operation until the General Election held upon the
dissolution of the first Parliament.
(2) If at the time of such dissolution the notification of
electoral districts has not been proclaimed as required by Article
97, the electoral districts for the first General Election to be held
upon the dissolution of the first Parliament, and the number of
Members which each such district shall be entitled to return by
virtue of the provisions of paragraph (4) of Article 96, shall be
as set out in the Sixth Schedule and accordingly, registers of
electors shall be prepared and certified for each such electoral
district, and unless Parliament otherwise provides, such registers
shall be prepared on the basis of the register of electors in force
immediately before the commencement of the Constitution.
|
|
Judges of Supreme
Court and High
Court to cease to
hold office |
|
163. All Judges of the Supreme Court and the High
Courts established by the Administration of Justice Law,
No.44 of 1973, holding office on the day immediately before
the commencement of the Constitution shall, on the
commencement of the Constitution, cease to hold office.
|
|
Continuation in
office of Judges,
public officers and
others
|
|
164. Subject to the provisions of Article 163 every person
who immediately before the Commencement of the Constitution -
(a) held office in any court or tribunal deemed, by
virtue of the provisions of paragraph (2) of
Article 105, to be a court or tribunal created and
established by Parliament,
(b) was in the service of the Republic, any local
authority or any Public Corporation,
(c) held office in any local authority or
Public Corporation, or
(d) held any appointment under any existing written
law,
shall continue in such service or hold such office
or appointment under the same terms and conditions.
|
|
Oath or
affirmation to be
taken or made by
public officers and
others |
|
165.
(1) Every public officer, judicial officer and every
other person as is required by the Constitution to take an oath or
make an affirmation on entering upon the duties of his office,
every holder of an office required under the existing law to take
an official oath and every person in the service of every local
authority and of every Public Corporation shall take and
subscribe the oath or make and subscribe the affirmation set out
in the Fourth Schedule. Any such public officer, judicial officer,
person or holder of an office failing to take and subscribe such
oath or make and subscribe such affirmation after the
commencement of the Constitution on or before such date as
may be prescribed by the Prime Minister by Order published in
the Gazette shall cease to be in service or hold office.
(2) The Minister in charge of the subject of Public
Administration may, in his sole discretion, permit any public
officer, judicial officer, person or holder of an office referred to
in paragraph (1) of this Article, to take the oath or make the
affirmation referred to in that paragraph after the prescribed
date if he is satisfied that the failure to take the oath or make the
affirmation within the time prescribed was occasioned by
illness or some other unavoidable cause. On his taking such
oath or making such affirmation, he shall continue in service or
hold office as if he had taken such oath or made such
affirmation within the time prescribed under paragraph (1) of
this Article.
(3) The President may by Proclamation –
(a) exclude the application of the provisions of
paragraph (1) of this Article to any
category of public officers,
(b) prescribe the persons or categories of
persons who may administer such oath or
affirmation in addition to the persons who
are empowered under the existing law to
administer oaths or affirmations.
|
|
Powers, privileges,
immunities and rights
of the Republic
|
|
166. Unless Parliament otherwise provides, the
Republic of Sri Lanka shall continue to possess and exercise
all powers, privileges, immunities and rights whatsoever
possessed, exercised or exercisable immediately prior to the
commencement of the Constitution.
|
|
Rights, duties and
obligations of the
Republic |
|
167. All rights and all duties or obligations, however
arising, of the Government of Sri Lanka and subsisting
immediately prior to the commencement of the Constitution
shall be rights, duties and obligations of the Government of
the Republic of Sri Lanka under the Constitution.
|
|
Past operation
of laws, previous Acts,
offences and pending
action, &c. |
|
168.
(1) Unless Parliament otherwise provides, all
laws, written laws and unwritten laws, in force
immediately before the commencement of the Constitution,
shall, mutatis mutandis and except as otherwise expressly
provided in the Constitution, continue in force.
(2) Save as otherwise provided in the Constitution,
existing laws, written laws and unwritten laws are not and
shall not in any manner be deemed to be provisions of the
Constitution.
(3) Wherever the Constitution provides that any law,
written law or unwritten law or any provision of the
Constitution shall continue in force until or unless
Parliament otherwise provides, any law enacted by
Parliament so providing may be passed by a majority of the
Member present and voting.
(4) Whenever the Constitution provides that any
provision of any existing written law shall continue in
force until or unless Parliament otherwise provides and
the existing written law referred to consists of subordinate
legislation, the provision that such existing written law
shall continue in force until or unless Parliament otherwise
provides shall not in any manner be deemed to derogate
from the power of the person or body on whom the power
to make and when made, to amend, vary, rescind or revoke
such subordinate legislation is conferred, to exercise the
power so conferred until or unless Parliament otherwise
provides.
(5) Unless the Constitution otherwise provides, the past
operation of any law in force prior to the commencement of the
Constitution or anything duly done or suffered or any offence
committed or any right, liberty, obligation or penalty acquired
or incurred under any law in force prior to the commencement
of the Constitution shall not in any manner be affected or be
deemed to be affected by the Constitution coming into force.
(6) All actions, prosecutions, proceedings, matters or
things, including proceedings of Commissions appointed or
established by or under any existing written law, pending or
uncompleted on the commencement of the Constitution shall,
subject to the provisions of the Constitution and mutatis
mutandis, be deemed to continue and may be carried on and
completed after the commencement of the Constitution.
|
|
Provisions
relating to
judiciary |
|
169. Unless Parliament otherwise provides –
(1) any provisions of the Administration of
Justice Law, No. 44 of 1973, which are
inconsistent with the provisions of the
Constitution, shall, to the extent of such
inconsistency, be deemed to be repealed;
(2) the Supreme Court established by the
Administration of Justice Law, No. 44 of
1973, shall, on the commencement of the
Constitution, cease to exist and accordingly
the provisions of that Law relating to the
establishment of the said Supreme Court, shall
be deemed to have been repealed. Unless
otherwise provided in the Constitution, every
reference in any existing written law to the
Supreme Court shall be deemed to be a
reference to the Court of Appeal;
(3) all appellate proceedings including proceedings
by way of revision, case stated and restitutio in
integrum pending in the Supreme Court
established under the Administration of Justice
Law, No. 44 of 1973, on the day preceding the
commencement of the Constitution, shall
stand removed to the Court of Appeal and the
Court of Appeal shall have jurisdiction to take
cognizance of and to hear and determine the
same; and the judgements and orders of the
Supreme Court aforesaid delivered or made
before the commencement of the Constitution
in appellate proceedings shall have the same
force and effect as if they had been delivered or
made by the Court of Appeal;
(4) all original proceedings by way of applications
for the issue of high prerogative Writs and
applications for any other relief pending in the
Supreme Court as well as all applications for
injunctions pending in the High Court established
under the Administration of Justice Law, No. 44 of
1973, on the date immediately preceding the
commencement of the Constitution shall stand
removed to the Court of Appeal and such Court
shall have jurisdiction to take cognizance of, hear
and determine or to continue and complete the
same, and the judgments and orders of the
Supreme Court established under the Administration
of Justice Law, No. 44 of 1973, delivered or made
before the commencement of the Constitution in
original proceedings shall have the same force and
effect as if they had been delivered or made by the
Court of Appeal:
Provided that any proceedings in relation to
any alleged breach of privileges of Parliament
pending in the Supreme Court shall stand removed
to the Supreme Court created and established by
the Constitution;
(5) no appeal shall lie from any judgement, order
or decree of the Supreme Court established under
the Administration of Justice Law, No. 44 of
1973, to the Supreme Court created and established
under the Constitution but such judgement, order or
decree, as the case may be, shall be final as between
the parties to the action, application or other
proceeding in which such judgement, order or
decree was made:
Provided that it shall be competent for the
Court of Appeal and all officers of such Court to
take all such steps as may be necessary,
including the entering of decrees if not already
entered and taxation and recovery of costs so as to
ensure that such judgements, orders and decrees
are completely and effectively complied with, as
if they had been delivered or made by the Court of
Appeal created and established by the Constitution;
(6) the several High Courts established under Chapter
I of the Administration of Justice Law, No. 44 of
1973, shall be deemed for all purposes to constitute a
single court created and established by
Parliament called the High Court of the Republic
of Sri Lanka having jurisdiction throughout the
Republic of Sri Lanka to be exercised in the
several Zones in accordance with the law for the
time being in force. Accordingly, subject to the
provisions of the Constitution, and of any existing
written law, all provisions relating to High Courts
contained in such Law shall, mutatis mutandis,
apply to the High Court of the Republic of Sri
Lanka;
(7) all criminal and admiralty cases, proceedings or
matters, other than applications for injunctions,
pending in the High Courts established under the
Administration of Justice Law, No. 44 of
1973, on the day preceding the commencement of
the Constitution shall stand removed to the said
High Court of the Republic of Sri Lanka and such
Court shall have jurisdiction to take cognizance of,
hear and determine or to continue and complete the
same, and the judgments and orders of the
aforesaid High Courts delivered or made before the
commencement of the Constitution shall have the
same force and effect as if they had been delivered
or made by the High Court of the Republic of Sri
Lanka;
(8) the President of the Court of Appeal shall
from time to time as he may deem expedient
nominate the Judges of the High Court of the
Republic of Sri Lanka to exercise the jurisdiction
of the High Court in such zones as he may
determine and the provisions of Chapter II of the
Administration of Justice Law, No. 44 of 1973,
shall mutatis mutandis, apply to the hearing and
disposal of all proceedings pending in or hereafter
instituted in the High Court;
(9) all indictments filed hereafter in the High Court
of the Republic of Sri Lanka shall be in the
name of the Republic of Sri Lanka and shall be
signed by the Attorney-General or any person
authorized under section 189 of the Administration
of Justice Law, No. 44 of 1973;
(10) all election petition proceedings relating to the
election of any person to the membership of the
National State Assembly pending in the High
Courts established under the Administration of
Justice Law, No. 44 of 1973, on the day
preceding the commencement of the Constitution
shall stand removed to the Court of Appeal and
the Court of Appeal shall have the same
jurisdiction to take cognizance of, hear and
determine or to continue and complete the same,
and the judgements and orders of the Supreme
Court established by the Administration of Justice
Law, No. 44 of 1973, and of the High Courts
aforesaid delivered or made before the
commencement of the Constitution in such election
petition proceedings shall have the same force and
effect as if they had been delivered or made by the
Supreme Court and the Court of Appeal established
by the Constitution, as the case may be. The
President of the Court of Appeal is hereby vested
with the power to nominate a Judge of the Court of
Appeal to hear and determine any election petition
in respect of which the Court of Appeal is vested
with jurisdiction by the Constitution;
(11) all attorneys-at-law admitted and enrolled or
deemed to have been admitted and enrolled as
attorneys- at-law under the provisions of the
Administration of Justice Law, No. 44 of 1973,
shall subject to the provisions of the Constitution
be deemed to have been admitted and enrolled as
attorneys-at-law of the Supreme Court created and
established by the Constitution;
(12) after the date fixed by the Minister in charge of
the subject of Justice, by Order published in the
Gazette, no attorney-at-law shall be entitled to
represent any party to a proceeding or be given the
right of audience in any court, tribunal or other
institution until or unless he has taken and
subscribed the oath or made and subscribed the
affirmation set out in the Fourth Schedule, before
a Judge of the Supreme Court, Court of Appeal,
High Court or any other judicial officer as
defined in Article 114; and it shall be the duty of
any such Judge or judicial officer, as the case
may be, to forward such oath or affirmation so
taken and subscribed or made and subscribed to
the Registrar of the Supreme Court who shall
cause the same to be entered in the rolls of such
Court. Such entry shall be the only proof that
such attorney-at-law has taken and subscribed or
made and subscribed such oath or affirmation;
(13) the provisions of the Administration of Justice
Law, No. 44 of 1973, relating to the AttorneyGeneral,
the legal profession, State Attorneys and
State Counsel, shall be deemed for all purposes to
be in operation, and every reference to the
Supreme Court in sections 33 to 36 of the
Administration of Justice Law, No. 44 of 1973,
and in the rules and regulations relating thereto
shall be deemed to be a reference to the Supreme
Court established by the Constitution;
(14) if any matter or question shall arise with regard
to any procedure or practice to be followed in any
court in consequence of the coming into
operation of the Constitution, not provided for
in the Constitution or any written law, the Chief
Justice shall have the power to give such
directions as he may consider necessary to
prevent injustice or as the justice of the case may
require and to ensure that the provisions of
Chapters XV and XVI of the Constitution are
given full and complete effect;
(15)
(i) any reference in section 2 of the Special
Presidential Commissions of Inquiry Law,
No.7 of 1978, to the Supreme Court shall be
deemed to be a reference to the Supreme
Court established by the Constitution;
(ii) where any person has been appointed as a
member of a Special Presidential Commission
of Inquiry established under the Special
Presidential Commission of Inquiry Law, No. 7
of 1978, then, such person shall notwithstanding
the provisions of the Constitution, continue
to be such member and shall be deemed for
the purposes of Article 81(1) to be a Judge
of a Court referred to therein unless he
resigns, or refuses or becomes unable to act,
or is discharged by the President from the
performance of his duties as such member in
accordance with the provisions of the
Special Presidential Commissions of Inquiry
Law, No. 7 of 1978;
(iii) any such member specified in the Warrant
establishing such Special Presidential
Commission of Inquiry as Chairman, shall,
subject to the provisions of sub-paragraph
(ii) of this paragraph, continue to be the
Chairman of such Special Presidential
Commission of Inquiry;
(16)
(i) any breach of the privileges of the National
State Assembly functioning immediately
prior to the commencement of the
Constitution, shall be deemed to be a breach
of the privileges of Parliament and
accordingly, Parliament and the Supreme
Court, shall have the power to take
cognizance of and punish any person for such
breach of privileges of Parliament;
(ii) where prior to the commencement of the
Constitution, any step required or authorized
by the Parliament (Powers and Privileges)
Act has been taken in respect of, or in
relation to, any act or omission alleged to
constitute such a breach of the privileges of
Parliament as is referred to in sub-paragraph
(i) of this paragraph, such step shall be
deemed to have been validly taken and any
further steps as are required or authorized
under such Act, may be taken, in respect of,
or in relation to, such alleged breach of the
privileges of Parliament, as if the act or
omission alleged to constitute such breach of
privileges of Parliament had been committed
or had occurred after the commencement of
the Constitution.
|
Provision relating
to Queen's Counsel
and Senior
Attorneys-at-Law
[4, 8 of 1984]
|
|
153[169A.
(1) Every –
(a) Queen’s Counsel appointed prior to the
coming into force of the Constitution; and
(b) Senior attorney-at-law appointed by the
President after the coming into force of the
Constitution,
shall, from the date on which this Article comes into
force, be called and known also as President’s Counsel and
shall continue to enjoy all such privileges as were hitherto
enjoyed by a Queen’s Counsel.
(2) Every rule made under Article 136 relating to the
appointment of Senior attorneys-at-law shall, from the date on
which this Article comes into force, be deemed to be rescinded.
(3) Every reference in any written law to “Senior attorney
-at- law” shall, from the date on which this Article comes into
force, be deemed to include a reference to “President’s
Counsel”.]
|
|
|
|
CHAPTER XXII
INTERPRETATION |
Interpretation
[22, 17 of 2001]
[57, 0 of 2020]
[6, 13 of 1987]
|
|
170. In the Constitution –
“civic disability” shall have the same meaning as in the
Special Presidential Commissions of Inquiry Law,
No. 7 of 1978, as on the commencement of the
Constitution;
“commencement of the Constitution” means the date
appointed by the Proclamation made under
Article 172;
“conclusion of the General Election” means the time at
which Members of Parliament for all the
electoral districts in respect of which a poll has
been taken on the date or dates specified in the
Proclamation made under Article 70(5) have been
declared elected by the respective returning
officers, or when on the results declared more than
half the total membership of Parliament consists
of Members belonging to any single recognized
political party or independent group, whichever
event occurs earlier;
“existing law” and “existing written law” mean any law
and written law, respectively, in force immediately
before the commencement of the Constitution
which under the Constitution continue in force;
“judicial officer”,154[other than in Article 111M], means
any person who holds office as -
(a) a Judge of the Supreme Court or a Judge of the
Court of Appeal;
(b) any Judge of the High Court or any Judge,
presiding officer or member of any other Court of
First Instance, tribunal or institution created and
established for the administration of Justice or for
the adjudication of any labour or other dispute
but does not include a person who performs
arbitral functions or a public officer whose
principal duty or duties is or are not the
performance of functions of a judicial nature.
No court or tribunal or institution shall have
jurisdiction to determine the question whether
a person is a judicial officer within the meaning
of the Constitution but such question shall be
determined by the Judicial Service Commission
whose decision thereon shall be final and
conclusive.
No act of such person or proceeding held before
such person, prior to such determination, shall
be, deemed to be invalid by reason of such
determination;
“law” means any Act of Parliament and any law enacted
by any legislature at any time prior to the
commencement of the Constitution and includes
an Order in Council;
“local authority” means any Municipal Council, Urban
Council, Town Council or Village Council and
includes any Authority created and established
by or under any law to exercise, perform and
discharge powers, duties and functions
corresponding to or similar to the powers, duties
and functions exercised, performed and
discharged by any such Council;
“public corporation” means any corporation, board or
other body which was or is established by or
under any written law other than the Companies
Ordinance, with funds or capital wholly or
partly provided by the Government by way of
grant, loan or otherwise;
155[“public officer” means a person who holds any paid
office under the Republic, other than a judicial
officer but does not include –
(a) the President;
(b) the Prime Minister;
(c) the Speaker;
(d) a Minister appointed under Article 44 or 45;
(e) a Deputy Minister appointed under Article 46;
(f) a Member of Parliament;
(g) a member of the Parliamentary Council;
(h) a member of the Judicial Service Commission;
(i) a member of any Commission referred to in Article 41A;
(j) the Commissioner-General of Elections;
(k) the officers appointed to the Election Commission,
by the Election Commission;
(l) the Secretary-General of Parliament;
(m) a member of the staff of the Secretary-General of
Parliament;
(n) a member of the University Grants Commission;
(o) a member of the Official Languages Commission;
(p) the Auditor-General; and
(q) the Parliamentary Commissioner for Administration
(Ombudsman).]
“recognized political party” means unless Parliament
otherwise provides, every political party which
is treated as a recognized political party under the
Ceylon (Parliamentary Elections) Order in Council,
1946;
“territorial waters” includes the territorial sea and the
historic waters of Sri Lanka;
“written law” means any law and subordinate legislation
156[and includes statutes made by a Provincial
Council, Orders], Proclamations, Rules, By-laws and
Regulations made or issued by any body or person
having power or authority under any law to make or
issue the same.
|
|
|
|
CHAPTER XXIII
REPEAL |
|
|
|
171.
The Constitution adopted and enacted on the 22nd day
of May, 1972, is hereby repealed.
|
|
|
|
CHAPTER XXIV
PROMULGATION OF THE CONSTITUTION |
|
Promulgation of
the Constitution |
|
172.
(1) The provisions of Chapter I to Chapter
XXIII shall come into force on the day appointed by the
President by Proclamation.
(2) Parliament shall meet on the day so appointed and
the President may, in such Proclamation, specify the time at
which Parliament shall so meet
Devo Vassatukalena
sassasampattihetu ca
phito bhavatu loko ca
raja bhavatu dhammiko
SIDDHIRASTU
|
|
|
|
* Other Consequential Amendments in the Twentieth
Amendment to the Constitution |
|
Transitional
Provisions |
|
58.
(1) Every person holding office on the day immediately
preceding the date of commencement of this Act, as –
(i) the Chief Justice;
(ii) Judges of the Supreme Court;
(iii) the members of the Judicial Service
Commission;
(iv) the President of the Court of Appeal;
(v) Judges of the Court of Appeal;
(vi) the Attorney-General;
(vii) the Auditor-General;
(viii) the Inspector-General of Police;
(ix) the Parliamentary Commissioner for Administration (Ombudsman);
(x) the Secretary-General of Parliament;
(xi) judges of the High Court; or
(xii) judicial officers, scheduled public officers,
public officers or police officers,
shall, unless he earlier resigns, dies or is removed from office
continue to hold such office and shall continue to exercise,
perform and discharge the powers, duties and functions of that
office under the same terms and conditions.
(2) Every person holding office on the day immediately
preceding the date of commencement of this Act as a member
of the Constitutional Council shall cease to hold such office
with effect from the date of commencement of this Act.
(3) Every person holding office on the day immediately
preceding the date of commencement of this Act as the
Chairman or a member of –
(a) the Election Commission;
(b) the Public Service Commission;
(c) the National Police Commission;
(d) the Human Rights Commission of Sri Lanka;
(e) the Commission to Investigate Allegations of
Bribery or Corruption;
(f) the Finance Commission; and
(g) the Delimitation Commission,
shall, unless he earlier resigns, dies or is removed from office
continue to exercise, perform and discharge the powers, duties
and functions of his office until such date on which the
respective Commissions are constituted in accordance with
Chapter VIIA of the Constitution.
(4) Every person holding office on the day immediately
preceding the date of commencement of this Act as the
Chairman or a member of –
(a) the Audit Service Commission; and
(b) the National Procurement Commission,
shall cease to hold such office with effect from the date of
commencement of this Act.
(5) Notwithstanding the provisions of subsection (4),-
(a) all suits, prosecutions, actions, proceedings,
matters or things which have been instituted by
or against the Audit Service Commission and
the National Procurement Commission and
which are pending as at the day immediately
preceding the date of commencement of this
Act shall, with effect from the date of
commencement of this Act, be deemed to be
suits, prosecutions, actions, proceedings,
matters or things which have been instituted by
or against the Government;
(b) any decree, order or award entered or made in
favour of or against the Audit Service Commission
and the National Procurement Commission by any
court or tribunal or other body in any action,
matter, proceeding or thing shall, with effect from
the date of commencement of this Act, be deemed
to be a decree, order or award entered or made in
favour of or against the Government and may be
enforced accordingly; and
(c) all property movable and immovable, belonging to
the Audit Service Commission and the National
Procurement Commission as at the day
immediately preceding the date of commencement
of this Act shall, with effect from the date of
commencement of this Act, vest in and be deemed
to be the property of the Government.
(6) All matters relating to the appointment, promotion,
transfer, disciplinary control and dismissal of members of the
Sri Lanka State Audit Service and pending before the Audit
Service Commission on the day immediately preceding the date
of commencement of this Act shall, with effect from that date,
stand transferred to the Public Service Commission and shall be
determined by the Public Service Commission accordingly.
(7) All matters pertaining to -
(a) the appointment, promotion, transfer,
disciplinary control and dismissal of police
officers; and
(b) appeals by police officers to the National
Police Commission,
pending before the National Police Commission on the day
immediately preceding the date of commencement of this Act, shall, with effect from that date, stand transferred to the Public
Service Commission and shall be determined by the Public Service Commission accordingly.
|
|
Avoidance of doubt
|
|
59. For the avoidance of doubt, it is hereby declared that
where there is a requirement in any written law to obtain the
recommendation or approval of the Constitutional Council, the
reference to the Constitutional Council shall be read and
construed as a reference to the Parliamentary Council.
|
FIRST SCHEDULE
ARTICLE 5
Names of Administrative Districts |
|
1 Colombo
2 Gampaha
3 Kalutara
4 Kandy
5 Matale
6 Nuwara - Eliya
7 Galle
8 Matara
9 Hambantota
10 Jaffna
157[5, 7 of 1983]
[11 Kilinochchi]
12 Mannar
13 Vavuniya
14 Mullaitivu
15 Batticaloa
16 Ampara
17 Trincomalee
18 Kurunegala
19 Puttalam
20 Anuradhapura
21 Polonnaruwa
22 Badulla
23 Moneragala
24 Ratnapura
25 Kegalle
|
SECOND
SCHEDULE
ARTICLE 6
|
|

THE NATIONAL FLAG
|
|
THIRD SCHEDULE
ARTICLE 7
Words and Music of the National Anthem



|
|
FOURTH SCHEDULE
ARTICLE 32, 53, 61, 107, 165

|
FIFTH SCHEDULE
ARTICLE 114(6) |
|
Clerks
158[7, 11 of 1987]
[Deputy Fiscals]
Interpreters
Stenographers
Typists
Binders
|
SIXTH SCHEDULE
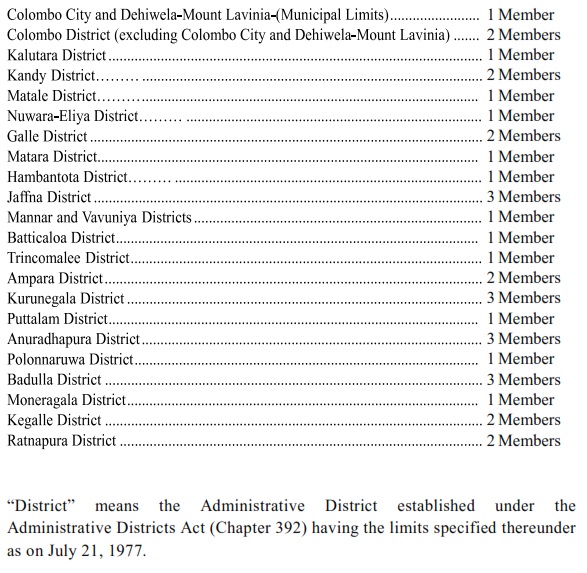
ARTICLE 162(2)
|
159[5, 6 of 1983]
SEVENTH SCHEDULE
ARTICLE 157A AND ARTICLE 161(d)

|
160[7, 13 of 1987]
[EIGHTH SCHEDULE
[ Article 154A ]
Provinces
|
|
Western
North-Western
Uva
Sabaragamuwa
Central
Eastern
Southern
North-Central
Northern]
|
161[7, 13 of 1987]
[NINTH SCHEDULE
LIST I
(Provincial Council List)
|
|
1. Police and Public order.– Public order and the exercise of police powers, to
the extent set out in Appendix I, within the Province, but not including National
Defence, National Security and the use of any armed forces or any other forces
under the control of the Government of Sri Lanka in aid of the civil power and not
including the city of Colombo, Sri Jayewardenepura, Kotte, and their environs the
limits of which shall be specified by the President by Order published in the Gazette.
2. Planning– Implementation of provincial economic plans.
3. Education and Educational Services.– Education to the extent set out in
Appendix III.
4. Local Government –
4:1 Local authorities for the purpose of Local Government and village
administration, such as Municipal Councils, Urban Councils and
Pradeshiya Sabhas, except that, the constitution, form and structure of
local authorities shall be determined by law;
4:2 Supervision of the administration of Local Authorities established by
law, including the power of dissolution (subject to such quasi-judicial
inquiries into the grounds for dissolution and legal remedies in respect
thereof, as may be provided by law and subject to provisions relating to
audit as may be provided by law);
4:3 Local Authorities will have the powers vested in them under existing law.
Municipal Councils and Urban Councils will have the powers vested in
them under the Municipal Councils Ordinance and the Urban Councils
Ordinance, Pradeshiya Sabha will have the powers vested in them
under existing law. It will be open to a Provincial Council to confer
additional powers on local authorities but not to take away their powers;
4:4 Gramodaya Mandalayas will have the powers vested in Gramodaya
Mandalayas under existing law. It will be open to a Provincial Council
to confer additional powers on Gramodaya Mandalayas.
5. Provincial Housing and Construction –
5:1 Implementing, co-ordinating, supervising and monitoring provincial
housing development programmes and projects (other than National
Housing Development Authority projects) including aided self- help
housing projects, housing loans and the provision of building materials;
5:2 The implementation of the Protection of Tenants Act and the Rent Act
within a Province;
5:3 Construction activity in respect of subjects in this List.
6. Roads and bridges and ferries thereon within the Province, other than–
(a) national highways;
(b) bridges and ferries on national highways
7. Social Services and Rehabilitation –
7:1 Probation and Child Care Services;
7:2 The Rehabilitation of destitute persons and families;
7:3 Rehabilitation and welfare of physically, mentally and socially
handicapped persons;
7:4 Relief of the disabled and unemployable
8. Regulation of road passenger carriage services and the carriage of
goods by motor vehicles within the Province and the provisions of interprovincial road transport services.
9. Agriculture and Agrarian Services –
9:1 Agriculture, including agricultural extension, promotion and education
for provincial purposes and agricultural services (other than in interprovincial irrigation and land settlement schemes, State land and
plantation agriculture);
9:2 Rehabilitation and maintenance of minor irrigation works;
9:3 Agricultural research save and except institutions designated as national agricultural research institutions.
10. Rural Development
11. Health –
11:1 The establishment and maintenance of public hospitals, rural hospitals,
maternity homes, dispensaries (other than teaching hospitals and
hospitals established for special purposes);
11:2 Public health services, health education, nutrition, family health
maternity and child care, food and food sanitation, environmental health;
11:3 Formulation and implementation of Health Development Plan and
of the Annual Health Plan for the Province;
11:4 The provision of facilities for all institutions referred to in 1 above
within the Province, excluding the procurement of drugs;
11:5 Awarding of Scholarships for Post-Graduate Education within
Sri Lanka to personnel attached to the Institutions specified in 1
above.
12. Indigenous Medicine – Ayurveda, Siddha and Unani –
12:1 Establishment of Ayurvedic dispensaries and hospitals, grants to
such dispensaries and hospitals;
12:2 Establishment and maintenance of herbaria;
13:1 Rest houses maintained by local authorities; and
13:2 Circuit bungalows presently administered by Government
departments whose functions are exclusively specified in this List.
14. Pawn brokers - Pawn brokers other than pawn brokers business carried on
by Banks.
15. Markets, fairs.
16. Food supply and distribution within the Province.
17. Co-operatives –
17:1 Co-operative undertakings and the organization, registration,
supervision and audit of co-operative societies within the Province;
17:2 Co-operative development within the Province including
co-operative education and propaganda;
17:3 Provincial Co-operative Employees Commission;
17:4 Matters connected with employment, promotion, retirement and
other connected matters of employees of co-operative societies
within the Province.
18. Land.– Land, that is to say, rights in or over land, land tenure, transfer and
alienation of land, land use, land settlement and land improvement, to the extent set
out in Appendix II.
19. Irrigation.– Planning, designing, implementation, supervision and
maintenance of all irrigation works, other than irrigation schemes relating to rivers
running through more than one Province or inter provincial irrigation and land
development schemes.
20. Animal husbandry.– Preservation, protection and improvement of stock
and prevention of animal diseases within the Province.
21. Subject to the formulation and implementation of National Policy in regard
to development and planning, the power to promote, establish and engage in
agricultural, industrial, commercial and trading enterprises and other incomegenerating projects, within the Province without prejudice to the power of the
Government and Public Corporations to have such enterprises and projects.
(This would include the promotion of scientific and industrial research
within the Province and the preparation, co-ordination and the implementation of
industrial development plans for the Province).
22. Reformatories, Borstal institutions and other institutions of a like nature
and persons detained therein, arrangements with other Provinces for the use of such
institutions.
23. Possession, transport, purchase and sale of intoxicating liquors.
24. Burials and burial grounds, cremations and cremation grounds, other than
those declared by or under law made by Parliament to be national memorial
cemeteries.
25:1 Libraries, Museums and other similar institutions controlled or
financed by a Provincial Council;
25:2 Ancient and historical monuments and records other than those
declared by or under law made by Parliament to be of national
importance.
26. The regulation of mines and mineral development, to the extent permitted
by or under any law made by Parliament, within the Province.
27. Incorporation, regulation and judicial winding up of corporations with
objects confined to the Province, excluding trading corporations, banking, insurance
and financial corporations.
28. Regulation of unincorporated trading, literary, scientific, religious and
other societies and associations.
29:1 Theatres and dramatic performances, music, cinemas,
entertainments and amusements, excluding the sanctioning of
cinematograph films for exhibition and public performances.
29:2 Encouragement and development of sports (other than national
sports associations).
30. Betting and gambling, other than imposition of licence fees and taxes.
31. Provincial debt.
32. Offences against statutes with respect to any of the matters specified in this
his List.
33. Fees in respect of any of the matters in this List, excluding fees taken in any
court.
34. Development, conservation and management of sites and facilities in the
Province for the generation and promotion of electrical energy (other than
hydro- electric power and power generated to feed the national grid).
35. The borrowing of money to the extent permitted by or under any law made
by Parliament.
36:1 Turnover taxes on wholesale and retail sales within such limits and
subject to such exemptions as may be prescribed by law made by
Parliament;
36:2 Betting taxes, and taxes on prize competitions and lotteries, other than
National Lotteries and lotteries organized by the Government of Sri
Lanka;
36:3 Licence taxes, arrack, toddy rents, tapping licence fees and liquor
licence fees;
36:4 Motor vehicle licence fees within such limits and subject to such
exemptions as may be prescribed by law made by Parliament;
36:5 Dealership licence taxes on drugs and other chemicals;
36:6 Stamp duties on transfer of properties, such as lands and motor cars;
36:7 Toll collections;
36:8 Fines imposed by courts;
36:9 Fees charged under the Medical Ordinance;
36:10 Fees charged under the Motor Traffic Act;
36:11 Departmental fees in respect of any of the matters specified in this List;
36:12 Fees under the Fauna and Flora Protection Ordinance;
36:13 Fees on lands alienated under the Land Development Ordinance and
Crown Lands Ordinance;
36:14 Court fees, including stamp fees on documents produced in court;
36:15 Regulatory charges under the Weights and Measures Ordinance;
36:16 Land revenue, including the assessment and collection of revenue and
maintenance of land records for revenue purposes;
36:17 Taxes on lands and buildings including the property of the State to the
extent permitted by law made by Parliament;
36:18 Taxes on mineral rights within such limits and subject to such
exemptions as may be prescribed by law made by Parliament;
36:19 Licensing fees on the possession, transport, purchase and sale of
intoxicating liquors;
36:20 Other taxation within the Province in order to raise revenue for
provincial purposes to the extent permitted by or under any law made
by Parliament.
37. Protection of environment within the Province to the extent permitted by or
under any law made by Parliament.
APPENDIX I
Law and Order
1. The subject devolved shall be described as follows:–
Public Order and the exercise of Police powers as set out in this Appendix
within the Province, but not including –
(a) national defence;
(b) national security; and
(c) the use of any armed forces or any other forces under the control of
the Government of Sri Lanka in aid of the civil power.
2. The I.G.P. shall be the head of the Sri Lanka Police Force, The
Sri Lanka Police Force shall be divided into –
(a) the National Division (including Special Units); and
(b) a Provincial Division for each Province.
2:1 The National Division shall consist of the I.G.P., (D.I.GG.,
S.S.PP., A.S.PP.,) and other ranks recruited at the national level.
2:2 A Provincial Division shall consist of the D.I.G., S.S.PP., S.PP
and A.S.PP., all seconded from the National Division and
Provincial Assistant Superintendents of Police, Chief Inspectors,
Inspectors, Sub-Inspectors, Sergeants and Constables recruited in
the Province. Members of the Provincial Division shall be eligible
for promotion to the National Division.
162[23, 17 of 2001]
[3. Recruitment to the National Police Division and promotion of Police
Officers in the Provincial Divisions to the National Division, shall be made by the
National Police Commission.]
3:1 The National Police Commission shall, before promoting any
police Officer serving in any Provincial Division to the National
Division, call for a Confidential Report on such Officer from the
relevant Provincial Police Commission and take the matters
specified in such report into consideration in deciding whether to
promote such Officer or not.
3:2 The Commission shall also be responsible for promotions, transfers
and disciplinary control of members of the National Division other
than the I.G.P. subject to paragraph 4:1 below.
3:3 It shall hear and determine appeals from officers seconded to
Provincial Divisions against whom disciplinary action has been
taken by Provincial Police Commissions.
3:4 It shall set standards for recruitment and promotion of Police
Officers of all Divisions and such standards shall be uniform for all
Provincial Divisions.
4. Recruitment to each Provincial Division shall be made by a Provincial
Police Commission composed of three members, namely -
(a) the D. I. G. of the Province;
(b) a person nominated by the Public Service Commission in
consultation with the President; and
(c) a nominee of the Chief Minister of the Province.
4:1 A Provincial Police Commission shall be responsible for transfers,
promotions and disciplinary control over officers in the Provincial
Division; for promotion of Officers of the National Division
seconded to the Provincial Division up to the rank of S.S.P.; and for
transfer and disciplinary control over officers seconded to the
Provincial Division, except the D.I.G.:
Provided that any Officer of the National Division seconded to
any Provincial Division against whom disciplinary action has been
taken by a Provincial Police Commission, shall have the right to
appeal to the National Police Commission, whose decision on such
appeal shall be final.
5. The National Police Commission or a Provincial Police Commission shall
be entitled to delegate such of its powers as may be prescribed to such other
person or authority as may be prescribed.
[23, 17 of 2001] 6. The I.G.P. shall appoint a D.I.G. for each Province with the concurrence of
the Chief Minister of the Province. However, where there is non agreement
between the Inspector-General of Police and the Chief Minister, the matter
163[will be referred to the National Police Commission], who, after due
consultations with the Chief Minister, shall make the appointment.
[23, 17 of 2001]
7. The cadres of Police Officers of all ranks of the National Division shall be
fixed by the Government of Sri Lanka. The cadre of Officers and other ranks of
each Provincial Division shall be fixed by the Provincial Administration
164[with the approval of the National Police Commission], having regard to –
(a) the area of the Province;
(b) population of the Province; and
(c) such other criteria, as may be agreed to or prescribed.
These principles shall be uniformly applied to all Provincial Divisions.
7:1 The cadres of the Provincial Divisions shall be fixed on
ascertained principles such as population, area, number of Police
Stations involved and other relevant considerations. These
principles shall be applied to all Provincial Divisions without
distinction.
7:2 The salary scales and perquisites of office enjoyed by the
various ranks in the National and Provincial Divisions shall be
determined by the Government of Sri Lanka after consultation
with the Chief Ministers of the Provinces. The salary scales
and perquisites of office as enjoyed by members of the
Provincial Divisions shall apply uniformly to all Provincial
Divisions.
8. The nature, type and quantity of fire-arms and ammunition and other
equipment for the National Division shall be determined by the National Police
Commission. The nature, type and quantity of fire-arms and ammunition and other
equipment for all Provincial Divisions shall be determined by the National Police
Commission after consultation with the Provincial Police Commission and uniform
standards and principles shall be applied for all Provincial Divisions.
9. Recruitment to the National Division shall be made at the ranks of P.C., S.I.,
and A.S.P., Recruitment to the Provincial Division shall be made at the ranks of
P.C., S.I., and P.A.S.P (rank referred to in paragraph 2:2 above).
9:1 Recruitment to the National Division shall be made by the
National Police Commission and recruitment to the Provincial
Division shall be made by the Provincial Police Commission
having regard to the standards of recruitment and other criteria
prescribed in this behalf:
Provided also that a recruit may, on appointment, set out
his preferences as to the Division in which he wishes to serve and
that he shall, if possible, be posted to the Division of his choice,
with the consent of the Division concerned.
9:2 The Government of Sri Lanka shall be responsible for the training
of all recruits to and of members of all Divisions of the Sri Lanka
Police Force.
165[23, 17 of 2001]
[The National Police Commission may, where he considers it
necessary provide for alternate training for members of any
Provincial Division.]
10. Members of the National Division and the Provincial Divisions shall wear
the same uniforms and insignia of rank, provided that uniforms of the members of
each Division shall bear a distinctive shoulder flash, indicating the Division to which
he belongs.
10:1 There shall be one uniformed police force in each Province,
comprising of the members of the Provincial Division and the
officers seconded thereto. Members of the National Division
shall ordinarily be in plain clothes provided that they may wear
uniforms when performing any duties in respect of the
maintenance or restoration of public order as set out in
paragraph 12:2, 12:3 and 12:4. Provided also that the I.G.P. and
such other Officers as may be specified shall ordinarily be
attired in uniforms.
11. All Police Officers serving in units of the National Division and
Provincial Divisions in any Province shall function under the direction and control
of the D.I.G. of such Province.
11:1 The D.I.G. of the Province shall be responsible to and under the
control of the Chief Minister thereof in respect of the
maintenance of public order in the Province and the exercise of
police powers in the Province as set out in this Schedule.
11:2 The provisions of paragraph 11:1 above are subject to the
qualifications that –
(a) upon the declaration of an emergency in the Province,
the President may assume such powers and
responsibilities of the Chief Minister and the Provincial
Administration in respect of public order within the
Province as he may, by regulation, provide; and
(b) where the President is of the opinion that the
security of or public order in a Province is threatened
by grave internal disturbance, he may, without the
declaration of an emergency, but in consultation with
the Chief Minister of such Province and subject to the
provisions of the Public Security Ordinance, by order,
deploy in aid of the civil power, any unit of the National
Division, in the Province for the purpose of restoring
public order:
Provided that every such order shall cease to be in force as soon
as the President is satisfied that public order has been restored or on
the expiry of thirty days from the date of the order, whichever is
earlier.
12:1 The Provincial Division shall be responsible for the preservation of
public order within the Province and the prevention, detection and
investigation of all offences (except the offences specified in the
Schedule) and subject to the powers of the Attorney-General in terms
of the Code of Criminal Procedure Act, the institution of prosecutions
in the relevant Courts in respect of such offences.
The National Division of the Sri Lanka Police Force shall be
responsible for the prevention, detection and investigation of all
offences specified in the Schedule and subject to the powers of the
Attorney-General in terms of the Code of Criminal Procedure Act, for
the institution of prosecutions in the relevant Courts in respect of such
offences.
12:2 Where the Chief Minister seeks the assistance of the National Division
to preserve public order within a Province, the I.G.P. shall deploy such
personnel of the National Division as are necessary for the purpose
and place them under the control of the D.I.G. of the Province.
12:3 Where a State of Emergency is declared in the Province, the I.G.P.
may deploy such units of the National Division as he deems necessary
in any Province for the restoration and maintenance of public order
within such Province.
12:4 Any offence which may ordinarily be investigated by a Provincial
Division may be investigated by the C.I.D. or any other unit of the
National Division –
(a) where the Chief Minister requests, that such investigation be
undertaken by the C.I.D. or any other unit of the National
Division; and
(b) where the I.G.P. is of opinion that an investigation of such
offence by the C.I.D. or any other unit of the National Division is
necessary, in the public interest and directs, after consultation
with the Chief Minister and the approval of the AttorneyGeneral, that such offence be investigated by the C.I.D. or any
other unit of the National Division.
13. The National Division shall perform all the functions vested in a Provincial
Division, in any Province, for a period of one year or until a Provincial Division is
established in such Province, whichever is earlier.
14. All Gazetted officers of the National Division and Provincial Division shall
be required to attain the prescribed standard in Sinhala and Tamil. All Officers of the
rank of A.S.P. and above shall also be required to attain the prescribed standard of
English.
Every recruit to the Sri Lanka Police Force shall have proficiency in his
mother tongue. For the first promotion he shall acquire proficiency in a language
other than his mother tongue. For the next promotion he shall acquire a knowledge
of the third language. The three languages recognized for this purpose are Sinhala,
Tamil and English.
SCHEDULE
List of Offences to be investigated by the National Police
1. Offences against the State.
2. Offences relating to the Navy, Army and Air Force.
3. Offences relating to the Elections.
4. Offences relating to Coins, Currency and Government Stamps.
5. Any Offence committed against the President.
6. Any Offence committed against a Public Officer, a Judicial Officer, or
the Speaker, or the Prime Minister or a Minister, or a Member of the Judicial
Service Commission, or a Member of the Public Service Commission or a
Deputy Minister or a Member of Parliament or the Secretary General of
Parliament or a Member of the President’s Staff or a Member of the Staff
of the Secretary-General of Parliament.
7. Any Offence relating to property belonging to the State or a State
Corporation or Company or Establishment, the whole or part of the
capital whereof has been provided by the State.
8. Any Offence prejudicial to National Security or the maintenance of
Essential Services.
9. Any Offence under any law relating to any matter in the Reserve List
other than such offences as the President may, by order published in the
Gazette, exclude.
10. Any Offence in respect of which Courts in more than one Province have
jurisdiction.
11. International Crimes.
APPENDIX II
Land and Land Settlement
State land shall continue to vest in the Republic and may be disposed of
in accordance with Article 33(d) and written law governing this matter.
Subject as aforesaid, land shall be Provincial Council Subject, subject to
the following special provisions:–
1. State land –
1:1 State land required for the purposes of the Government in a
Province, in respect of a reserved or concurrent subject may be
utilised by the Government in accordance with the laws governing
the matter. The Government shall consult the relevant Provincial
Council with regard to the utilisation of such land in respect of
such subject.
1:2 Government shall make available to every Provincial Council State
land within the Province required by such Council for a Provincial
Council subject. The Provincial Council shall administer, control
and utilise such State land, in accordance with the laws and statutes
governing the matter.
1:3 Alienation or disposition of the State land within a Province to any
citizen or to any organisation shall be by the President, on the
advice of the relevant Provincial Council, in accordance with the
laws governing the matter.
2. Inter-Provincial Irrigation and Land Development Projects.
2:1 Such projects would comprise irrigation and land development
schemes –
(a) within the Province initiated by the State and which utilize
water from rivers flowing through more than one Province; a
Provincial Council however, may also initiate irrigation and
land development schemes within its Province utilizing water
from such rivers;
(b) within the Province which utilize water through diversions
from water systems from outside the Province; and
(c) all schemes where the command area falls within two or more
Provinces such as the Mahaweli Development Project.
2:2 These projects will be the responsibility of the Government of Sri
Lanka.
2:3 The principles and criteria regarding the size of holdings of
agricultural and homestead lands arising out of these projects will
be determined by the Government of Sri Lanka in consultation
with the Provincial Councils.
2:4 The selection of allottees for such lands will be determined by
the Government of Sri Lanka having regard to settler selection
criteria including degree of landlessness, income level, size of
family and agricultural background of the applicants. The actual
application of these principles, selection of allottees and other
incidental matters connected thereto will be within the powers of
the Provincial Councils.
2:5 The distribution of all allotments of such land in such projects
will be on the basis of national ethnic ratio. In the distribution of
allotments according to such ratios, priority will be given to
persons who are displaced by the project, landless of the District
in which the project is situated and thereafter the landless of the
Province.
2:6 Where the members of any community do not, or are unable to
take their entitlements of allotments from any such project, they
would be entitled to receive an equivalent number of allotments
in another Inter-Provincial Irrigation or Land Development
Scheme. This unused quota should be utilized within a given
time-frame.
2:7 The distribution of allotments in such projects on the basis of the
aforesaid principles would be done as far as possible so as not to
disturb very significantly the demographic pattern of the
Province and in accordance with the principle of ensuring
community cohesiveness in human settlements.
2:8 The administration and management of such projects will be done
by the Government of Sri Lanka.
3. National Land Commission.
3:1 The Government of Sri Lanka shall establish a National Land
Commission which would be responsible for the formulation of
national policy with regard to the use of State land. This
Commission will include representatives of all Provincial
Councils in the Island.
3:2 The National Land Commission will have a Technical Secretariat
representing all the relevant disciplines required to evaluate the
physical as well as the socio-economic factors that are relevant to
natural resources management.
3:3 National policy on land use will be based on technical aspects
(not on political or communal aspects), and the Commission will
lay down general norms in regard to the use of land, having
regard to soil, climate, rainfall, soil erosion, forest cover,
environmental factors, economic viability, &c.
3:4 In the exercise of the powers devolved on them, the powers shall
be exercised by the Provincial Councils having due regard to the
national policy formulated by the National Land Commission.
APPENDIX III
Education
1. Provision of facilities for all State Schools other than specified schools
(Specified Schools will be National Schools, Special Schools for
Service Personnel and schools for specified development schemes).
2. Supervision of the management of –
(a) all pre-schools; and
(b) all State schools other than specified schools indicated above.
(In order to ensure standards the Ministry of Education will retain the
right to inspect and supervise the management of schools).
3. The transfer and disciplinary control of all educational personnel,
i.e. Teachers, Principals and Education Officers, Officers belonging
to a National Service but serving the Provincial Authority on
secondment will have the right of appeal to the Public Service
Commission. Officers belonging to the Provincial Public Service will
have a right to appeal to the Public Service Commission against
dismissal.
4. Recruitment into the Teaching Service of those with diplomas and
degrees, from Colleges of Education and Universities, recognised as
teaching qualifications.
5. Until adequate numbers of these categories are available recruitment
into the Teaching Service will be on the results of recruitment
examinations conducted by the Public Service Commission. On the
results of these examinations interviews and selection will be
conducted together with the Provincial Authorities.
6. Appointment of Principals of all schools other than those in
1A, B, C categories. (Criteria will be laid down by the Minister of
Education).
7. Appointment of Principals of 1A, B, C schools will be by the Secretary
to the Ministry of the Minister in charge of the subject of Education of
the Public Service Commission.
8. Training of teachers and other educational personnel will come within
the purview of the National Institute of Education. Provincial
Authorities will indicate their needs to the National Institute of
Education.
9. Appointment of Provincial Boards of Education which will have the
advisory functions, will be the responsibility of the Minister of
Education. However, this will be done with the concurrence of the
Chief Minister of the Provincial Authority
10. Provincial Authorities will establish School Boards conforming to the specifications laid down by the Ministry of Education.
11. Provincial Authorities will supervise the working of School Boards.
12. Preparation of plans (educational development plan and annual implementation plan) will be the responsibility of the Provincial Authority.
13. Implementation of the Annual Education Development Plan.
14. Appraisal of the performance of Principals, Teachers and Education Officers.
15. Conducting of in-service training programmes for which prior approval of the National Institute of Education has been obtained.
16. Conducting of local examinations approved by the Commissioner-General of Examinations.
17. Implementation of non-formal education programmes.
18. Registration and supervision of pre-schools.
19. Obtaining the approval of the National Institute of Education for local variations in the primary curriculum and selected subjects in the secondary curriculum.
20. Construction and maintenance of educational buildings, libraries and playgrounds.
21. Procuring and distribution of teaching aids,visual aids and audio visual materials, furniture and other equipment.
22. Procuring and distribution of science equipment other than certain specified items indicated by the Ministry.
23. Production and distribution of school text books after approval by the Ministry.
24. Organization and development of school libraries in accordance with guidelines given by the National Library Services Board.
(Above based on the recommendations of Committee I of the Political Parties Conference)
LIST II
(Reserved List)
National Policy on all Subjects and Functions.
Defence and National Security: Internal Security; Law and order and prevention and
detection of crime except do the extent specified in item 1 of List I.
This would include –
(a) Defence of Sri Lanka and every part thereof including preparation for
defence and all such acts as may be conducive in times of war to its
prosecution and after its termination, to effective demobilisation;
(b) Naval, military and air forces; any other armed forces of the
Government of Sri Lanka;
(c) Deployment of any armed force of the Government of Sri Lanka or any
other force subject to the control of the Government of Sri Lanka or any
contingent or unit thereof in any Province in aid of the civil power;
powers, jurisdiction, privileges and liabilities of the members of such
forces while on such deployment;
(d) Delimitation of cantonment areas, local self-government in such areas,
the constitution and powers within such areas of cantonment authorities
and the regulation of house accommodation (including the control of
rents) in such areas;
(e) Naval, military and air force works;
(f) Arms, firearms, ammunition and explosives;
(g) Atomic energy and mineral resources necessary for its production
(h) Industries declared by Parliament by law to be necessary for the purpose
of defence or for the prosecution of war;
(i) Criminal Investigation Department;
(j) Preventive detention for reasons connected with Defence, Foreign
Affairs, or the security of Sri Lanka, persons subjected to such detention;
and
(k) Extension of the powers and jurisdiction of members of a police
force belonging to any Province to any area outside that Province, but
not so as to enable the police of one Province to exercise powers and
jurisdiction in any area outside that Province without the consent of
the Provincial Council in which such area is situated; extension of the
powers and jurisdiction of members of a police force belonging to
any Province to railway areas outside that Province.
Foreign Affairs
This would include –
(a) Foreign Affairs; all matters which bring the Government of Sri Lanka
into relation with any foreign country;
(b) Diplomatic, consular and trade representation;
(c) United Nations Organization;
(d) Participation in international conferences, associations and other bodies
and implementing of decisions made thereat;
(e) Entering into treaties and agreements with foreign countries and
implementing treaties, agreements and conventions with foreign
countries;
(f) War and peace; and
(g) Foreign jurisdiction.
Posts and Telecommunications; Broadcasting; Television
This would include –
(a) Posts and telegraphs; telephones; wireless, broadcasting and other like
forms of communications; and
(b) Sanctioning of cinematograph films for exhibition.
Justice in so far as it relates to the judiciary and the courts structure.
This would include –
(a) Constitution, organisation, jurisdiction and powers of the Supreme
Court (including contempt of such Court) and the fees taken therein;
persons entitled to practise before the Supreme Court, Court of Appeal
and other Courts;
(b) Constitution, organisation, jurisdiction and powers of the Court of
Appeal and the fees taken therein; and
(c) Jurisdiction and powers of all Courts, except the Supreme Court and
the Court of Appeal.
Finance in relation to national revenue, monetary policy and external resources;
customs.
This would include –
(a) Public debt of the Government of Sri Lanka;
(b) Currency, coinage and legal tender; foreign exchange;
(c) Foreign loans;
(d) Central Bank;
(e) National Savings Bank;
(f) Lotteries organised by the Government of Sri Lanka or a Provincial
Council;
(g) Banking;
(h) Bills of exchange, cheques, promissory notes and other like instruments;
(i) Insurance;
(j) Stock exchanges and future markets;
(k) Audit of the accounts of the Government of Sri Lanka and of the
Provinces;
(l) Taxes on income, capital and wealth of individuals, companies and
corporations;
(m) Customs duties, including import and export duties and excise duties;
(n) Turnover taxes and stamp duties, except to the extent specified in List I;
(o) Any other tax or fee not specified in List I.
Foreign Trade; Inter-Province Trade and Commerce
This would include –
(a) Trade and commerce with foreign countries; import and export across
customs frontiers; definition of customs frontiers; and
(b) Inter-province trade and commerce.
Ports and Harbours
This would include –
(a) Ports declared by or under law made by Parliament or existing law to
be major ports including their delimitation and the constitution and
powers of port authorities therein; and
(b) Port quarantine, including hospitals connected therewith; seamen’s and
marine hospitals.
Aviation and Airports
This would include –
Airways; aircraft and air navigation; provision of aerodromes; regulation and
organisation of air traffic and of aerodromes; provision for aeronautical
education and training and regulation of such education and training
provided by Provinces and other agencies.
National Transport
This would include –
(a) Railways;
(b) Highways declared by or under law made by Parliament to be
national highways; and
(c) Carriage of passengers and goods by railway, land, sea or air or by
national waterways in mechanically propelled vessels.
Rivers and Waterways; Shipping and Navigation; Maritime zones including
Historical Waters, Territorial Waters, exclusive Economic zone and Continental Shelf
and Internal Waters; State Lands and Foreshore, Except to the Extent Specified in
Item 18 of List I.
This would include –
(a) Piracies and crimes committed on the high seas or in the air; offences
against the law of nations committed on land or the high seas or in the
air;
(b) Shipping and navigation on inland waterways, declared by Parliament
by law to be national waterways, as regards mechanically propelled
vessels; the rule of the road on such waterways;
(c) Maritime shipping and navigation, including shipping and navigation
on tidal waters; provision of education and training for the mercantile
marine and regulation of such education and training provided by
Provinces and other agencies;
(d) Lighthouses, including lightships, beacons and other provision for
the safety of shipping and aircraft;
(e) Regulation and development of inter province rivers; and river valleys
to the extent to which such regulation and development under the
control of the Government of Sri Lanka is declared by Parliament by
law to be expedient in the public interest;
(f) Fishing and fisheries beyond territorial waters; and
(g) Property of the Government of Sri Lanka and the revenue therefrom,
but as regards property situated in a province, subject to statutes made
by the Province save in so far as Parliament by law otherwise provides.
Minerals and Mines
This would include –
(a) Regulation and development of oil fields and mineral oil resources;
petroleum and petroleum products; other liquids and substances declared
by Parliament by law to be dangerously inflammable; and
(b) Regulation of mines and mineral development to the extent to
which such regulation and development under the control of the
Government of Sri Lanka is declared by Parliament by law to be
expedient in the public interest.
Immigration and Emigration and Citizenship
This would include –
(a) Citizenship, Naturalization and Aliens;
(b) Extradition; and
(c) Admission into and emigration and expulsion from, Sri Lanka;
passports and visas.
Elections Including Presidential, Parliamentary, Provincial Councils and Local
Authorities
This would include –
Elections to Parliament, Provincial Councils, Local Authorities and to the
Office of President; the Department of Elections.
Census and Statistics
This would include –
(a) Census; and
(b) Inquiries, surveys and statistics for the purposes of any of the matters
in this List.
Professional Occupations and Training
This would include –
(a) Institutions, such as Universities, declared by Parliament by law to
be institutions of national importance;
(b) Institutions for scientific or technical education by the Government of
Sri Lanka wholly or in part and declared by Parliament by law to be
institutions of national importance;
(c) Provincial agencies and institutions for –
(i) professional, vocational or technical training, including the
training of police officers; or
(ii) the promotion of special studies or research; or
(iii) scientific or technical assistance in the investigation or
detection of crime; and
(d) Co-ordination and determination of standards in institutions for
higher education or research and scientific and technical institutions.
National Archives; Archaeological Activities and Sites and Antiquities declared by or
under any law made by Parliament to be of National Importance.
This would include –
Ancient and historical monuments and records and archaeological sites and
remains declared by or under law made by Parliament to be of national
importance.
All Subjects and Functions not Specified in List I or List III including –
(a) Pilgrimages to places outside Sri Lanka;
(b) Incorporation, regulation and winding up of trading corporations,
including banking, insurance and financial corporations but not
including co-operative societies;
(c) Incorporation, regulation and winding up of corporations, whether
trading or not, with objects not confined to one province, but not
including universities;
(d) Patents, inventions and designs; copyright, trade marks and merchandise
marks;
(e) Establishment of standards of weight and measure;
(f) Establishment of standards of quality for goods to be exported out of
Sri Lanka or transported from one province to another;
(g) Industries, the control of which by the Government of Sri Lanka is
declared by Parliament by law to be expedient in the public interest;
(h) Regulation of labour and safety in mines;
(i) Manufacture, supply and distribution of salt by agencies of the
Government of Sri Lanka; regulation and control of manufacture, supply
and distribution of salt by other agencies;
(j) Cultivation, manufacture and sale for export, of opium;
(k) Industrial disputes concerning employees of the Government of Sri Lanka;
(l) Institutions such as Museums and War Memorials financed by
the Government of Sri Lanka wholly or in part and declared by
Parliament by law to be institutions of national importance;
(m) The Survey of Sri Lanka, the Geological, Botanical, Zoological and
Anthropological Surveys of Sri Lanka; Meteorological organizations;
(n) National Public Services; National Public Service Commission;
(o) Pensions, that is to say, pensions payable by the Government of Sri
Lanka or out of the Consolidated Fund;
(p) Salaries and allowances of Members of Parliament and the Speaker
and Deputy Speaker of Parliament;
(q) Powers, privileges and immunities of Parliament and of the members and
the Committees of Parliament; enforcement of attendance of persons for
giving evidence or producing documents before Committees of
Parliament or Commissions appointed by Parliament;
(r) Emoluments, allowances, privileges and rights in respect of leave
of absence, of the President and Governors; salaries and allowances of
the Ministers of the Government of Sri Lanka; the salaries, allowances
and rights in respect of leave of absence and other conditions of service
of the Auditor-General;
(s) Inter-Province migration; inter-province quarantine;
(t) Offences against laws with respect to any of the matters in this List; and
(u) Fees in respect of any of the matters in this List, but not including fees
taken in any Court.
LIST III
(Concurrent List)
1. Planning –
1:1 Formulation and appraisal of plan implementation strategies at the
provincial level;
1:2 Progress control;
1:3 Monitoring progress of public and private sector investment programmes;
1:4 The evaluation of the performance of institutions and enterprises engaged
in economic activities;
1:5 The presentation of relevant data in the achievement of plan targets;
1:6 The dissemination of information concerning achievement of plan targets;
1:7 Publicity of implementation programmes;
1:8 Manpower planning and employment Data Bank;
1:9 Nutritional planning and programmes.
2. and 3. Education and Educational Services.– Education, except to the extent
specified in items 3 and 4 of List 1.
4. Higher Education –
4:1 The establishment and maintenance of new Universities.
4:2 The establishment of degree awarding institutions under the Universities
(Amendment) Act, No. 07 of 1985 and other institutions for tertiary,
technical and post-school education and training.
5. National Housing and Construction.– The promotion of integrated planning and
implementation of economic, social and physical development of urban development
areas.
6. Acquisition and requisitioning of Property.
7. Social Services and Rehabilitation –
7:1 Relief, rehabilitation and resettlement of displaced persons;
7:2 Relief of distress due to floods, droughts, epidemics or other exceptional
causes and rehabilitation and resettlement of those affected;
7:3 Restoration, reconstruction and rehabilitation of towns, villages, public
institutions and properties, industries, business places, places of
worship and other properties destroyed or damaged, grant of
compensation or relief to persons or institutions who have sustained
loss or damage and the reorganization of civil life.
8. Agricultural and Agrarian Services –
8:1 Establishment and promotion of agro-linked industries, the establishment
and maintenance of farms and supervision of private nurseries;
8:2 Soil conservation;
8:3 Plant pests.
9. Health –
9:1 Schools for training of Auxiliary Medical Personnel;
9:2 The supervision of private medical care, control of nursing homes
and of diagnostic facilities within a Province;
9:3 Population control and family planning;
9:4 Constitution of Provincial Medical Boards.
10. Registration of births, marriages and deaths.
11. Renaming of Towns and Villages.
12. Private lotteries within the Province.
13. Festivals and Exhibitions.
14. Rationing of food and maintenance of food stocks.
15. Co-operatives – Co-operative Banks.
16. Surveys – For the purpose of any of the matter enumerated in the Provincial or Concurrent List.
17. Irrigation –
17:1 Water storage and management, drainage and embankments, flood
protection, planning of water resources;
17:2 Services provided for inter-provincial land and irrigation schemes,
such as those relating to rural development, health, education,
vocational training, co-operatives and other facilities.
18. Social Forestry and protection of wild animals and birds.
19. Fisheries - Other than fishing beyond territorial waters.
20. Animal Husbandry –
20:1 Production, processing, distribution and sale of livestock and
livestock products;
20:2 Veterinary training services and research, inclusive of the provision of
science laboratories and science equipment;
20:3 Animal breeding, care and health;
20:4 The establishment of pastures.
21. Employment –
21:1 Employment planning at Provincial level;
21:2 Special Employment programmes relating to the Province;
21:3 Promotion of youth employment activities relating to the Province;
21:4 Technical Manpower Development Programmes in relation to the Province.
22. Tourism.– Development and control of the Tourist Industry in the Province.
23. Trade and commerce in, and the production, supply and distribution of –
(a) the products of any industry where the control of such industry by
the Government is declared by Parliament by law to be expedient in
the public interest and imported goods of the same kind as such
products; and
(b) foodstuffs and cattle fodder
24. Newspapers, books and periodicals and printing presses.
25. Offences against statutes with respect to any matters specified in this List.
26. Fees in respect of any of the matters in this List, excluding fees taken in any
Court.
27. Charities and charitable institutions, charitable and religious endowments and
religious institutions.
28. Price control.
29. Inquiries and statistics for the purpose of any of the matters in this List or in the
Provincial Council List.
30. Adulteration of foodstuffs and other goods.
31. Drugs and Poisons.
32. Extension of electrification within the Province and the promotion and
regulation of the use of electricity within the Province.
33. Protection of the environment.
34. Archaeological sites and remains, other than those declared by or under any law
made by Parliament to be of national importance.
35. Prevention of the extension from one Province to another of infectious or
contagious diseases or pests affecting human beings, animals or plants.
36. Pilgrimages.]
|
|
1 - Substituted by the Seventh Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2(a) for "twenty four"
2 - Substituted by the Seventh Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2(b) for "territorial waters".
3 - Inserted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2.
4 - Renumbered as paragraph (1)by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2(a).
5 - Inserted by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2(b).
6 - Substituted by the Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2(1) for “or a Member of a Local Authority”.
7 - Substituted by the Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2(2) for “or in such Local Authority”.
8 - Article 22 substituted by the Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3
9 - Article 23 substituted by the Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3.
10 - Article 24(1) substituted by the Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(1).
11 - Substituted by the Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(2) for “in either of the National Languages”.
12 - Substituted by the Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(3) (a) for “the appropriate National Language”.
13 - Substituted by the Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(3)(b) for “either of the National Languages.”
14 - Substituted by the Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(4) for “the use of National Languages.”
15 - Inserted by the Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 5.
16 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3.
17 - Inserted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(1).
18 - Inserted by the Third Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2 (1).
19 - Substituted by the Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2(2)(a).
20 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(2)(a)(i) for “commencement of
his current term of office”.
21- Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2 for “by election for a further
term”.
22 - Repealed by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(2)(a)(ii).
23 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(2)(b) for “six years”.
24 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(2)(b) for “six years”.
25 - Substituted by the Third Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2(2).
26 - Substituted by the Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3(1).
27 - Inserted by the Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3(2).
28 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3.
29 - Repealed by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4.
30 - Article 35 substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 5.
31 - Substituted by the Third Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3 for '"one month".
32 - Chapter VII A substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 6 for “Constitutional Council”.
33 - Chapter VIII substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 7.
34 - Original Chapter IX substituted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4.
35 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 8(1).
36 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 10.
37 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 8(2) for “with the approval of the Constitutional
Council”.
38 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 10(3).
39 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 8(3) for "such period, on the
recommendation of the Constitutional Council”.
40 - Original Article 55 substituted by the Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 8.
41 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 11 for "as are specified by the Cabinet of
Ministers”.
42 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 12 for "as are specified by the Cabinet of Ministers”.
43 – Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 13 for "Subject to the provisions of Paragraph
(1), (2), (3), (4) and (5) of Article 126”.
44 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 9 for “the affirmation set out in the Fourth
Schedule to the Constitution”.
45 - Articles 61E and 61F substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 10.
46 - Substituted by the Fourteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3.
47 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 15.
48 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 11(1).
49 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 11(2).
50 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 12.
51 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 13(1) for the word “fourteen”.
52 - Inserted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 13(2)
53 - Substituted by the Fourteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4 for “duly approved by the
People at a Referendum”.
54 - Inserted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 14 which was repealed by the Nineteenth Amendment
to the Constitution.
55 - Substituted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 6 for "Article 116".
56 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 15(1).
57 - Sec. (vii) - (xii) substituted for Sec. (vii) - (x) by the Ninth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2.
58 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 20(2) for "a public officer holding any office".
59 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 20(3) for "a public officer holding any office".
60 - Inserted by Sec. 7(4) of the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution.
61 - Repealed by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 15(2) which was inserted by the Nineteenth
Amendment to the constitution.
62 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 16 for "thirty five".
63 - Inserted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 20, which was repealed by the Eighteenth
Amendment to the Constitution.
64 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 17 for “paragraph (1) of this
Article”.
65 - Substituted by the Seventh Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3 for "Twenty Four"
66 - Repealed by the Fifteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2 which was inserted by the Fourteenth
Amendment to the Constitution.
67 - Substituted by the Fourteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 6 and by the Fifteenth
Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3.
68 - Substituted by the Fourteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 7.
69 - Substituted by the Fifteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(1) for "less than one eighth of the
total votes".
70 - Article 99(14) Repealed by the Fifteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(2).
71 - Article 99A inserted by the Fourteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 8.
72 - Inserted by the Fifteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 5.
73 - Substituted by the Sixth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2 for "by election or otherwise".
74 - Repealed by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 8 and new Chapter XIV A
"Election Commission" is inserted by Sec. 9.
75 - New Chapter XIVA (Articles 103-104J) inserted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 9.
76 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 18(1).
77 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 18(2).
78 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 23 for paras (4),(4a) and (5).
79 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 19(1).
80 - Inserted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 19(2).
81 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 19(3).
82 - Substituted by the Twentieth amendment to the Constitution Sec. 20(1).
83 - Substituted by the Twentieth amendment to the Constitution Sec. 20(2) for “Sixty five”.
84 - Inserted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 25.
85 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 21.
86 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 22.
87 - Substituted by the Eleventh Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2.
88 - Substituted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 12(1).
89 - Inserted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 12(2).
90 - Inserted by the Seventh Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4.
91 - Substituted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 13 for the words “the president
may, by warrant, appoint”.
92 - Inserted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 14.
93 - Article 116 renumbered as article 111C by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 15.
94 - Chapter XV A, Articles 111D to 111M, inserted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution
Sec. 16.
95 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 28.
96 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 23 for “subject to the approval of
the Constitutional Council”.
97 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 24.
98 - Articles 112, 113, 113A, 114, 115 and 117 repealed by the Seventeenth Amendment to the
Constitution Sec. 17.
99 - Renumbered as Article 111C by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 15.
100 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 25 for “ten”.
101 - Inserted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 26.
102 - Inserted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 27.
103 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 28 for the figures “120 & 121”.
104 - Inserted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 29.
105 - Marginal note substituted by the Fourteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 9(3) for "election petitions".
106 - Substituted by the Fourteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 9(1) for "election of the President".
107 - Substituted by the Fourteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 9(2) for "election of the President shall be"
108 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 30 for the figures "121 & 125".
109 - Words "and the appointment of senior Attorneys-at-law" omitted by the Eighth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3.
110 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 31 for the word “eleven”.
111 - Substituted by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3(a) for "committed by any Court of First Instance”.
112 - Substituted by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3(b) for "of which such Court of First Instance”
113 - Inserted by the First Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2 w. e. f. 7th September 1978.
114 - Substituted by the Eleventh Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 6.
115 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 32(1).
116 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 32(2).
117 - Articles 153A to 153H Repealed by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 33-40.
118 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 36.
119 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 41.
120 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 36(2) for the words “public corporation or
business or other undertaking”.
121 - Substituted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 36(3) for the words "any public corporation
or business or other undertaking”
122 - Inserted by the Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 36(4).
123 - Chapter XVIIA inserted by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4.
124 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 42 .
125 - Inserted by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 5.
126 - Paras (8) and (9) repealed by the Tenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec.2(1).
127 - Paras (10) & (11) renumbered as (8) & (9) by the Tenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2(2).
128 - Substituted by the Tenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2(3) for “contained in paragraph (6),
(7), (8) or (9) of this Article”.
129 - New Chapter XVIIIA inserted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 20.
130 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 43 (1).
131 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 43(2).
132 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 44(1) for “four”.
133 - Repealed by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 44(2).
134 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 45.
135 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 46.
136 - Inserted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 47, which was originally inserted
by Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution and repealed by the Nineteenth amendment to the
Constitution.
137 - Inserted by the Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 27.
138 - Repealed by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec.48 - 52.
139 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 53.
140 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 54(1).
141- Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 54(2).
142 - Chapter XIXA repealed by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 55.
143 - Chapter XIXB repealed by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 56.
144 - Article 157A inserted by the Sixth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 3.
145 - Substituted by the Third Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4 for “shall hold office”
146 - Substituted by the Second Amendment to the Constitution Sec 2.
147 - Substituted by the Sixth Amendment to the Constitution Sec 4(1) for "to fill such vacancy. Upon receipt of such
nomination, the Commissioner".
148 - Inserted by the Fifth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2(b).
149 - Substituted by the Sixth Amendment to the Constitution, Sec. 4(2)(a), for “within thirty days of
his being required to do so”.
150 - Substituted by the Sixth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(2)(b), for “vacancy, then the
Commissioner of Elections”.
151 - Inserted by the Sixth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4(3)
152 - Substituted by the Fourth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 2.
153 - Inserted by the Eighth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 4.
154 - Substituted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 22(1) for "other than in Article 114".
155 - Substituted by the Twentieth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 57.
156 - Substituted by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 6 for the words "and includes
orders".
157 - Inserted by the Seventh Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 5(a) and renumbered by Sec. 5(b)
158 - Substituted by the Eleventh Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 7 for “Fiscals.”
159 - Inserted by the Sixth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 5.
160 - Inserted by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 7.
161 - Inserted by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 7.
162 - Substituted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 23(1)
163 - Substituted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 23(2) for "will be referred to the President”.
164 - Substituted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 23(3), for “with the approval of the President”.
165 - Substituted by the Seventeenth Amendment to the Constitution Sec. 23(4) for “The President may, where he
considers it necessary provide for alternate training for members of any Provincial Division”.
|
|